
- How to disable ipv6 on mac os x how to#
- How to disable ipv6 on mac os x install#
- How to disable ipv6 on mac os x manual#
- How to disable ipv6 on mac os x full#
The syntax is essentially the same, just replace the special route ::/0 with a more specific in the same prefix/length notation that is specific for IPv6.
How to disable ipv6 on mac os x how to#
With IPv6, remember the special destination in this case is ::/0, which means “ all routes“ How to set a generic route for IPv6 on Mac $ sudo route add -inet6 2a02:69e0::/32 2003:c8:b711:300:::1Īpart from one default route, we might have the need for additional more specific routes or special routes, that are reachable via a different path than the default route. On MacOS, if you set a default route via a Link-Local address (fe80::), you have to add the outgoing interface with %interface (like in the above example -> %en0) to the command, or else the operating system cannot know which interface is facing the default router!Ī default route is probably the most important route for a host, because it acts as a catch-all route and all traffic that is not sent to another “more specific” destination is sent here… How to configure a default route for IPv6 on Mac $ sudo route add -inet6 ::/0 fe80::ee:7e0d:8941:1be5 %en0
How to disable ipv6 on mac os x full#
Check out man ndp for full functionality or this very similar FreeBSD ndp man page. Ndp is the MacOS tool to control and diagnose the IPv6 neighbor discovery protocol. How to display the neighbor cache for IPv6 on Mac $ ndp -a

Verify correct removal with ifconfig, e.g.
To remove an address, just add the delete word and drop the alias word. How to remove a static address for IPv6 on Mac in Terminal $ sudo ifconfig en0 inet6 delete 2003:c8:b711:300:c18:348e:7db5:9999 prefixlen 64 You need the sudo command to do this system level change, unless you are already root (su), which your regular user account should not be. You can get the output from only one single interface with the following command: $ ifconfig en0 How to configure a static address for IPv6 on Mac in Terminal $ sudo ifconfig en0 inet6 2003:c8:b711:300:c18:348e:7db5:9999 prefixlen 64 alias
How to disable ipv6 on mac os x install#
Like stated before, you can also install the iproute2 GNU packages from homebrew to gain access to the regular GNU utils if you prefer those. I still wanted to provide this semi-full output for you to be able to read and understand the different IPv6 addresses in this MacBook Pro which is just connected to WiFi. From what you have learned this far, you should be able to make sense of them all. I excluded about 80% of other output from this command, because it is really long. Inet6 fe80::1%lo0 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x1 The following commands are all built-in MacOS commands, no additional 3rd party components! How to display addresses for IPv6 on Mac in Terminal $ ifconfig lo0: flags=804 I like to have some of my favorite “gnutils” handy on my Mac. There are also CLI commands for MacOS that I would like to show you.īe aware, that in general you can use most open source GNU core utilities also on a Mac by installing homebrew. Usually the option selected will be Automatic on a regular client.
How to disable ipv6 on mac os x manual#
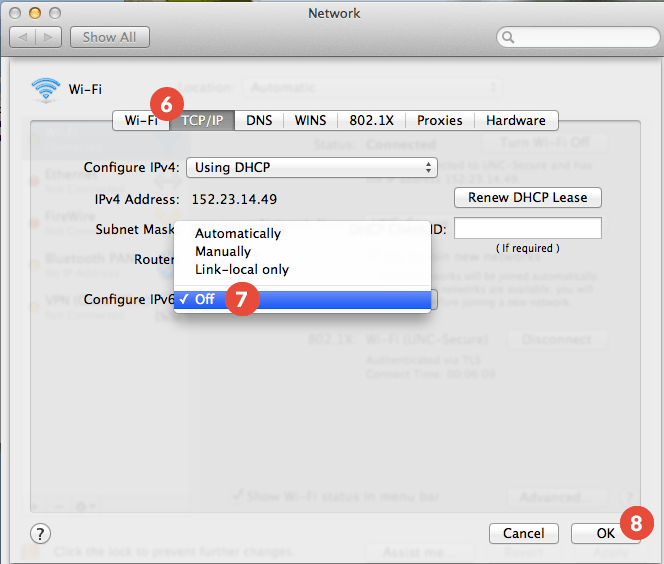
The screenshot above has a manual configuration using the graphical user interface (GUI) highlighted.

By default IPv6 on Mac OS, is enabled and does not have to be configured manually, unless you want to. Let’s have a look at IPv6 support and some history for Microsoft Windows, Apple MacOS and Linux implementations of our new Internet Protocol.įor sure, Apple MacOS or previously OS X has also been early to adopt IPv6 and its implementation in Catalina, Mojave and other recent versions can today be called complete and stable.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
